Note
We recommend using the target board, which supports meta-layer files for the Yocto build, but this is not required.
We recommend using the target board, which supports meta-layer files for the Yocto build, but this is not required.
A bring-up process is a series of tasks to migrate a specific platform to a new System on a Chip (SoC) board. A common bring-up process consists of the following tasks:
This page describes how to bring up webOS OSE from scratch.
The following picture shows a brief summary of the bring-up process.
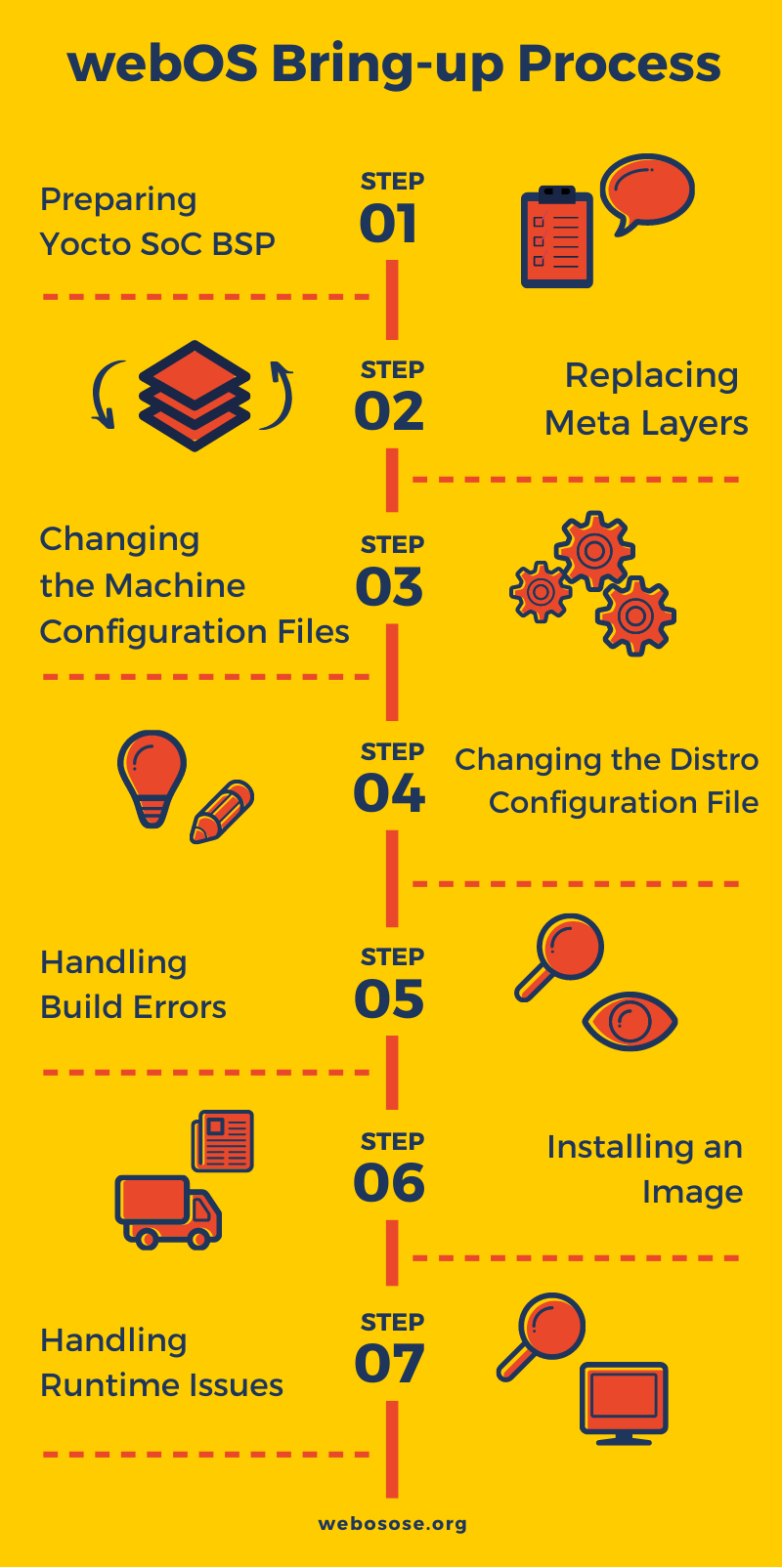
Preparing Yocto SoC BSPs:
First, you need to prepare BSP for your SoC board. The BSP files contain information to support specific hardware. These files are usually provided by SoC makers and depend on the type of your SoC board.
Replacing meta-layers:
A meta-layer is a set of files that determine how to build a target. You need to add, change, and remove meta-layers specific to your hardware target.
Changing the machine configuration files:
A machine configuration determines your target SoC board. Examine the machine configuration files and make necessary changes, such as the boot loader, kernel, and image size, to support your hardware target.
(Optional) Changing the distribution configuration file:
A distribution configuration determines policy configurations for your distribution. If you want to distribute webOS OSE, you can use webOS OSE’s distribution configuration file.
Handling build errors
Modify the recipe files to fix build errors.
Installing an image
Modify or add tasks to create an image format that is installable on your SoC board.
Handling runtime errors
Correct errors during running webOS OSE. Before starting this step, make sure that you understand the execution sequences of Luna Surface Manager (LSM) and Web Application Manager (WAM).
For more details on the bring-up process, see the Yocto Project Manual.
Once you’ve done the bring-up process, you can go through the following checklist to see if the bring-up was successful.
If all the steps work fine, then you succeed in bringing up webOS OSE.
Contents