Note
FOTA using libostree is not supported for the emulator.
FOTA using libostree is not supported for the emulator.
From version 2.0.0, webOS Open Source Edition (OSE) supports Firmware-Over-the-Air (FOTA) based on libostree.
This page outlines the FOTA solution and describes how to set up the environment to use the feature.
libostree is an upgrade system for Linux-based operating systems, which performs atomic upgrades of complete filesystem trees. The underlying architecture might be summarized as “git for operating system binaries”. At its core is a git-like content-addressed-object store with branches (or “refs”) to track meaningful filesystem trees within the store. Similarly, one can check out or commit to these branches. That is, libostree is both a shared library and suite of command line tools that combines a “git-like” model for committing and downloading bootable filesystem trees.
So, libostree can contain several “sysroots” at the same time and can jump to another version without extra flashing. But because it uses hardlink-based approach, the disk usage will increase only by the difference between upgrades.
To boot a specific version from filesystem trees, libostree requires additional sequence on the bootloader. (e.g. For Raspberry Pi, libostree uses u-boot and initramfs)
For more technical details, see the libostree project documentation.
When building webos-image, libostree creates a libostree repository and push rootfs into the repository.
This is similar to committing rootfs to git repo. If you commit rootfs to git repo when you build webos-image, the repo will have a history of image creation, and you can check out the rootfs of a specific version at any time. In other words, you can download a rootfs from libostree repo to a webOS device, and easily upgrade the platform version by commanding libostree to deploy the rootfs.
The following describes how to configure libostree repo and upgrade version.
On the build machine, set up your own libostree repository for FOTA.
Install the tool for managing a libostree repository.
$ sudo apt install libostree-1-1
Install an HTTP server from which to download data to a webOS device.
$ sudo apt install apache2
$ sudo a2enmod userdir
$ mkdir -p ~/public_html/ostree/repo
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2.service
Set the libostree repository path.
OSTREE_REPO = "{absolute path of target directory}" to webos-local.conf.$ cd build-webos
$ echo "OSTREE_REPO = \"\${HOME}/public_html/ostree/repo\"" >> webos-local.conf
Build the webos-image. As a result of webos-image build, rootfs will be pushed to ${OSTREE_REPO} automatically.
$ source oe-init-build-env
$ bitbake webos-image
# to check ostree log
$ ostree log --repo=$HOME/public_html/ostree/repo webos-image-master
On the target device, take the following steps to upgrade the image using libostree.
Add the remote repository:
ostree remote add --no-gpg-verify {repository name} {URL}
| Example |
|---|
|
Pull from the remote repository:
ostree pull --commit-metadata-only --depth={depth} {repository name} {branch name}
--commit-metadata-only: don’t download actual files
--depth: number of commits to pull. (-1: unlimited)
| Example |
|---|
|
Check the libostree commit log:
ostree log {repository name}:{branch name}
| Example |
|---|
|
Deploy a specific revision, and reboot the target.
ostree admin switch {repository name}:{commit hash value}
| Example |
|---|
|
Check the booted revision:
ostree admin status
The asterisk in the displayed result indicates currently booted revision.
| Example |
|---|
|
libostree creates a read-only bind mount over /usr. So it provides a command in /usr to remove the read-only bind mount and replace it with a writable overlay file system.
It supports two modes: development mode and hotfix mode.
Development mode : loses all changes when reboot
root@raspberrypi4:/# ostree admin unlock
Hotfix mode : changes will remain after reboot
root@raspberrypi4:/# ostree admin unlock --hotfix
Development mode : Just reboot.
Hotfix mode : Deploy the other revision.
Check the deployments available to be booted into: ostree admin status
root@raspberrypi4:# ostree admin status
* webos c4c72bce3d9bbf145dee7aa914224d4ae071e51b9f156466bddfe98476d2e568.0
Unlocked: hotfix
origin refspec: c4c72bce3d9bbf145dee7aa914224d4ae071e51b9f156466bddfe98476d2e568
Deploy the desired deployment with refspec and reboot.
root@raspberrypi4:/# ostree admin deploy c4c72bce3d9bbf145dee7aa914224d4ae071e51b9f156466bddfe98476d2e568
root@raspberrypi4:/# reboot
libostree does not provide rollback by single line command.
Refer to the figure below for understanding. From the perspective of libostree, disabling the hotfix mode is the same as upgrading to a new revision.
Even if you try to deploy to the revision you just used, libostree creates a new directory for the deployment root, such as /ostree/deploy/webos/deploy/AAA.1 (AAA.0 already exists), from its repository.
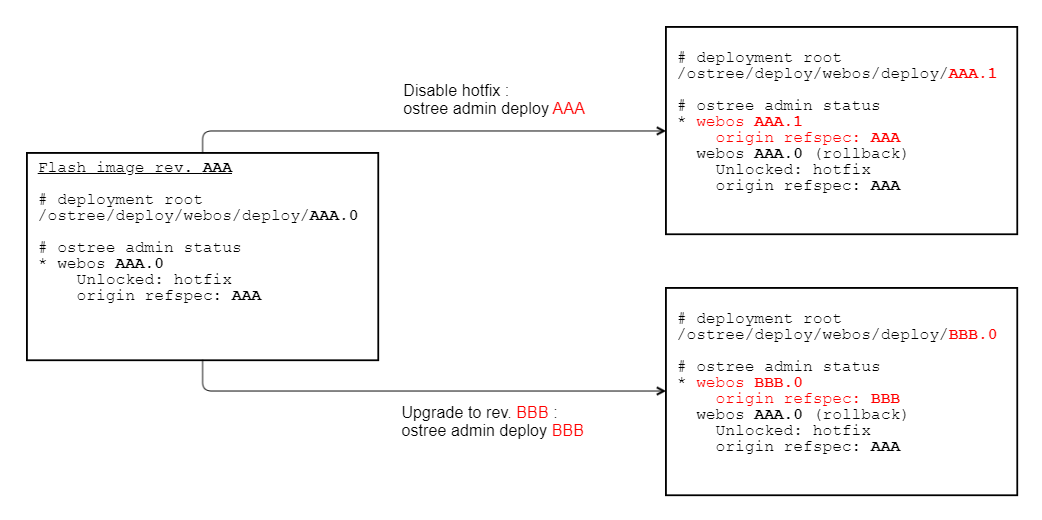
So this appendix explains how to manually rollback to the previous deployment.
Check deployments and their order. (In the example below, there are 2 deployments.)
root@raspberrypi4:/# ostree admin status
* webos 36b78bbacc3209aa0373483d57288bd4f50249af8c46917cda55fe6740a3f755.4 # 1st deployment (asterisk means current booted deployment)
origin refspec: 36b78bbacc3209aa0373483d57288bd4f50249af8c46917cda55fe6740a3f755
webos 6d32e91a9d2251c74f81088db729522d53c0e9271dbf9d604f74bcd1a7f8de71.2 (rollback) # 2nd deployment
Unlocked: hotfix
origin refspec: 6d32e91a9d2251c74f81088db729522d53c0e9271dbf9d604f74bcd1a7f8de71
Swap the boot configuration of the current booted deployment with the desired deployment to rollback.
The /boot/loader/uEnv.txt contains 3 key-values for each deployment: kernel_imageX, ramdisk_imageX, and bootargsX, as shown in the example below.
And these are listed in the order of the deployments identified by ostree admin status above.
Modify only the suffix values X for kernel_imageX, ramdisk_imageX and bootargsX keys.
root@raspberrypi4:/# vi /boot/loader/uEnv.txt
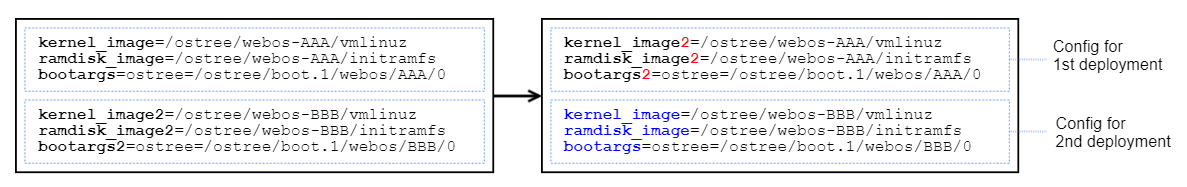
Reboot.
root@raspberrypi4:/# reboot
Contents