Object Detection Using YOLOv3
February 18, 2022
Overview of Project
This project is to implement an object detection model application by using You Only Look Once v3 (YOLOv3) to identify and locate objects by means of voice command. Suppose a user asks the app about the whereabouts of an object.
- If the object is present, the app, with the help of Google Text-to-Speech (TTS), informs the user about the total number of objects found and their directions. For example, the model reports, “The cup is present to your left but close to the center.”
- If the object is not present, an audio file is played saying, “The object you are searching for is not found.”
This model can help a visually impaired user to find objects easily as shown in the following scenarios:
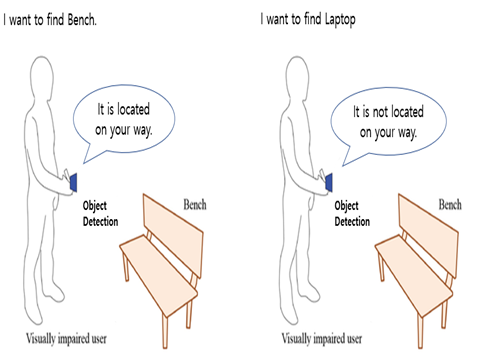
Required object found (left-hand side image):
- A visually impaired user asks the app to find a bench.
- The app detects the bench in front and indicates that it is found.
Required object NOT found (right-hand side image):
- A visually impaired user asks the app to find a laptop.
- The app does not detect any laptop devices and indicates that it is not found.
Object Detection Model
The object detection model is executed according to the following steps:
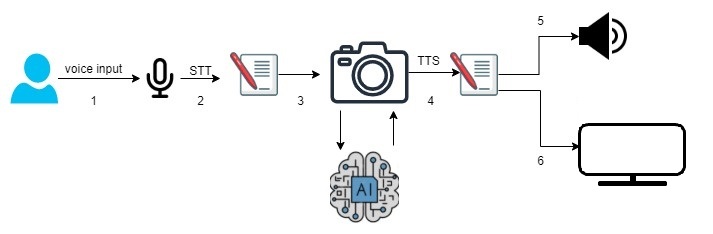
- A user speaks through the microphone to search for an object.
- The user speech is converted to text by using Google Speech-to-Text (STT).
- The trained YOLOv3 model is used for object detection.
- The object specified by the user is matched with the objects found.
- The app speaks out the status of the objects found (their presence and directions).
- The app displays the photo of the object.
Prepare a Target device
You must prepare a target device, Raspberry Pi 4 (RPi 4), flashed with a webOS OSE image. Set your device up by performing the instructions mentioned at Building webOS OSE. After you have performed the procedure, you have a fully functional webOS OSE target device. Note down the IP address of the device.
Note
On the target device, create a Google account. This Google account is used later to configure the required Google services.
Connect Hardware Devices
You need to connect the following items to the target device:
- USB headphone
- HD USB camera (better resolution required for better image detection)
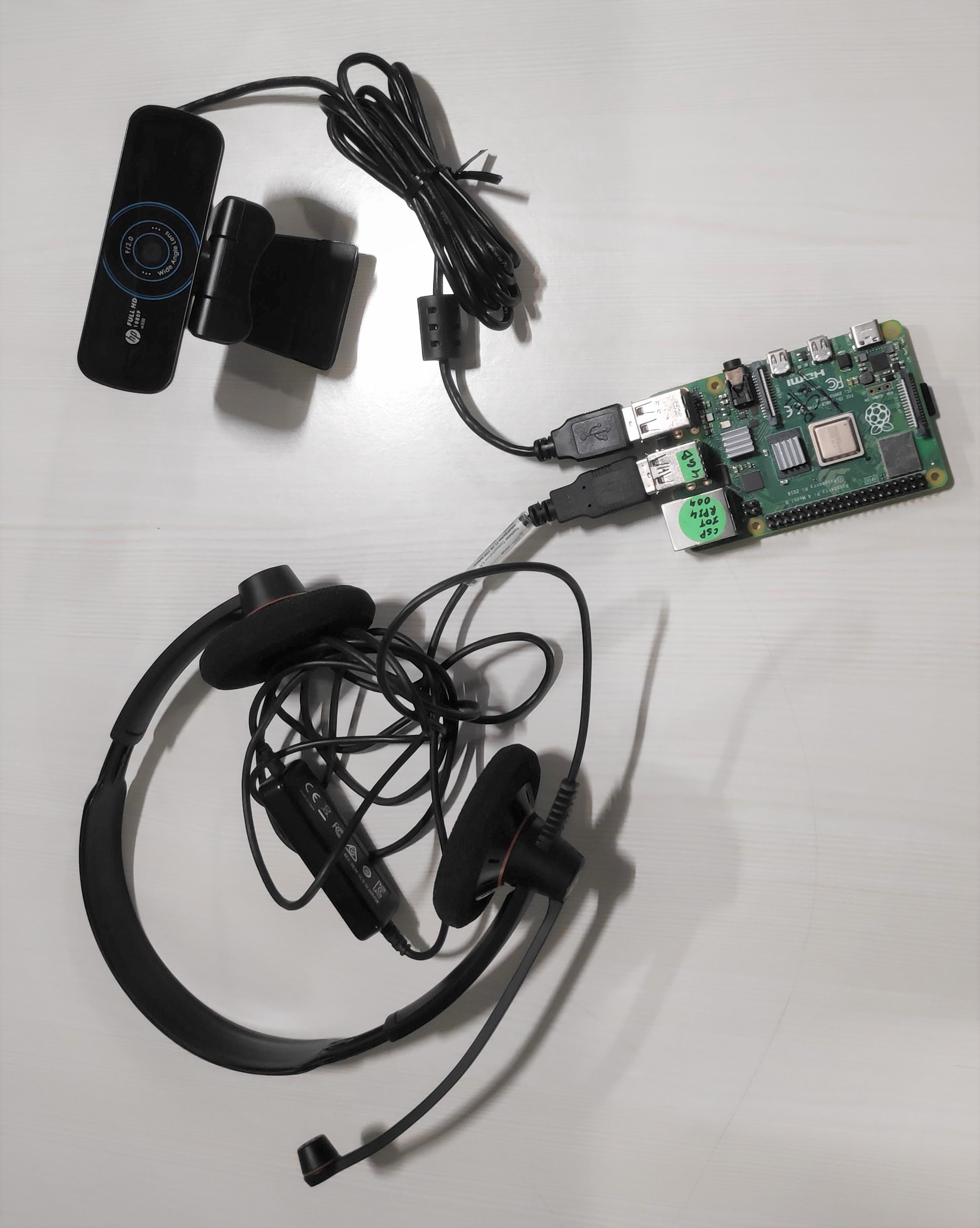

Configure the audio output device. By default, the audio output is played on the USB headset. However, if you want the output on a Bluetooth speaker, follow these steps:
Connect to the target device.
Create a file named .asoundrc at path ~/ and add the following content:
pcm.!default {
type asym
playback.pcm {
type plug
slave.pcm pulse
}
capture.pcm {
type plug
slave.pcm "hw:1,0"
}
}
This is an audio configuration file that handles playback audio on the runtime pulse availability of the audio device that is attached to the target device. For example, Bluetooth speakers and USB headsets.
Save the file.
Download YOLO Components
On the target device, prepare the following directories:
- Create a directory named
ObjectDetection in the /home/root/ directory. - Create a directory named
picture in the /home/root/ObjectDetection/ directory. - Create a directory named
ObjectDetectionImage in the /media/internal/ directory to store processed images.
You also need to download the following package files to the target device:
| yolov3.cfg | The number of (output) channels of a layer is given by "filters" (as each filter produces one channel). The neural network model architecture is stored in the yolov3.cfg file. Go to the project directory. cd /home/root/ObjectDetection/Download the yolov3.cfg file. wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pjreddie/darknet/master/cfg/yolov3.cfg
|
| yolo.weights | YOLO divides up the image into a grid of 19x19 cells: Each of these cells is responsible for predicting 5 bounding boxes. This network divides the image into regions and predicts bounding boxes and probabilities for each region. These bounding boxes are weighted by the predicted probabilities. The pre-trained weights of the neural network are stored in this file. Go to the project directory. /home/root/ObjectDetection/Download the yolo.weights file. wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
Note
File Size is big (around 150 MB) wait till download. |
| coco.names | Contains the names of the objects supported by the YOLO model. Go to the project directory. cd /home/root/ObjectDetection/Download the coco.names file. wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pjreddie/darknet/master/data/coco.names
|
Install Python3 Packages
You need to install some python packages on the target device. For easy installation of these packages, run the easy_setup.sh script as described below:
Connect to the target device.
Download the required shell script.
$ wget http://www.github.com/webosose/samples/blob/master/poc-apps/easy_setup.sh
Give execution permission to the shell script.
$ chmod 777 easy_setup.sh
Run the shell script to install the required Python packages.
A service account is a special type of Google account intended to represent a non-human user that needs to authenticate and be authorized to access data in Google APIs. Typically, service accounts are used in scenarios such as running workloads on virtual machines (VMs).
Follow these steps to prepare your Google service account and set up your services:
Use the Google account you have created when preparing the target device to log in to the Google Cloud Platform Console.
Select an existing project or create a new project and proceed with the remainder of the Google service configurations.
Create a service account according to the following steps:
- From the Google Cloud Console navigation menu, choose IAM & Admin > Service Accounts, then click + CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNT.
- In the Service account name field, enter a name.
- The Service account ID field is automatically updated based on this name.
- In the Service account description field, enter a description. For example, “Service account for quickstart”.
- Click CREATE AND CONTINUE.
- Click Select a role field. Under Quick access, select Basic > Owner, and click CONTINUE.
- Click DONE to finish creating the service account.
Add a service account key to your service account according to the following steps:
Click on the name of the Email address which has just been created from Step 3.
In the KEYS tab, click ADD KEY, then click Create new key.
Select Key type as JSON (default selected), then click CREATE. A JSON key file is downloaded to your local PC.
Save the key file and click CLOSE.
Rename the downloaded JSON file on your local PC to gstt.json.
Copy the gstt.json file to the /home/root/ObjectDetection/ directory of the target device.
Go to the /home/root/ObjectDetection/ directory on the target device and enable the key by running the following command:
$ export GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS="/home/root/ObjectDetection/gstt.json"
Enable Google Speech-to-Text (STT).
- Select the existing project that you created above.
- In the search bar, type “Cloud Speech-to-Text API”.
- Click on the “Cloud Speech-to-Text API” search result.
- Click ENABLE.
- Click ENABLE BILLING > CREATE BILLING ACCOUNT to create your billing account.
Enable Google Text-to-Speech (TTS).
- Select the existing project that you created above.
- In the search bar, type “Cloud Text-to-Speech API”.
- Click on the “Cloud Text-to-Speech” search result.
- Click ENABLE.
- Click ENABLE BILLING > CREATE BILLING ACCOUNT to create your billing account.
Caution
You may be charged depending on your usage of the TTS and STT services.
Install the App
Install the app on the target device by using the webOS OSE CLI from your local PC.
On your local PC, follow these steps:
Install the webOS OSE CLI.
$ npm install -g @webosose/ares-cli
Register the target device.
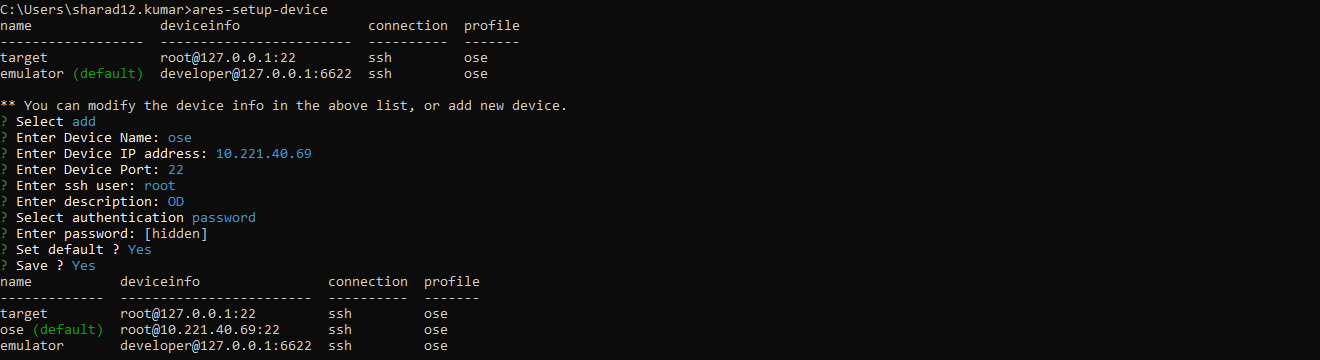
As shown in the above figure, select the add option and fill in the details of your RPi4 device and type “yes” for Save.
Download the following IPK to your local PC: com.app.objectviewer_0.0.1_all.ipk.
Go to the directory where the IPK is downloaded, and install the IPK on the target device.
$ ares-install --device target com.app.objectviewer_0.0.1_all.ipk
Launch the App
On the target device, launch the installed app by following these steps:
Go to the app directory.
$ cd /home/root/ObjectDetection/
Download the CamImage.py file and copy it to the /home/root/ObjectDetection/ directory.
Run the app.
Specify the object to be found by stating the hot word as “LG”. For example, “LG find umbrella and bottle.”
An image that labels all the identified objects, is displayed on the monitor via the app.
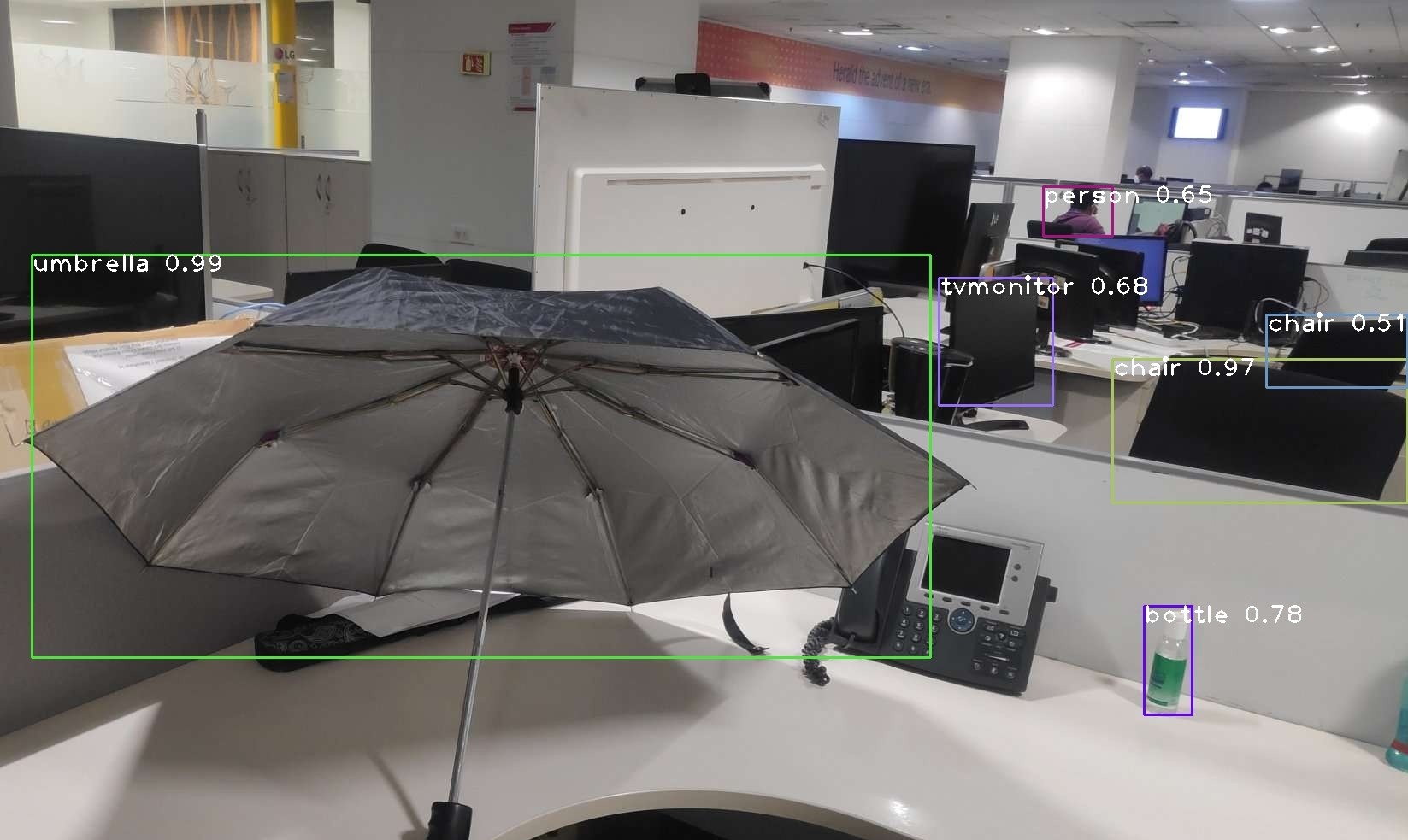

You can see that the umbrella and bottle are identified.
If the object requested by the user is present in the image, the audio output is “Umbrella found towards the left, bottle found towards right”. If the object is not present, the audio output is “Umbrella and bottle not found”.
Code Implementation
The source code for the object detection app is available at the samples git repository. To get a deeper understanding, refer to the snippets provided below, which explain some important parts of the implementation.
Importing Libraries
Includes the necessary libraries on the target device when the program runs and executes.
import cv2
import numpy as np
import requests
import os
import pyaudio
import wave
from collections import Counter
talk()
This function helps to convert a text file into mp3 audio file and plays it to the user.
- This function is called with the passed parameter “text”, which contains the output text.
- This function calls the Google TTS library then converts the text into mp3 file.
- The mpg123 player plays the converted mp3 file.
def talk(text):
from gtts import gTTS
import os
mytext = text
language = 'en'
myobj = gTTS(text=mytext, lang=language, slow=False)
myobj.save("welcome.mp3")
os.system("mpg123 " + "welcome.mp3")
take_alter_command()
This function is called when the user makes voice command.
This function calls the voicein function recursively until it collects the right input from the user.
The voicein function sets the parameters, such as chunk and frame, to record the voice.
This function initiates recording for 5 seconds and stops recording. After that, the recording is saved as a .wav file.
With the help of Google Cloud, this function converts the .wav audio file to the text.
If the user has not given any input voice, then the text must be empty and this functions repeatedly calls the voicein function.
If the text is not empty, it gets converted into a lowercase text.
From the lowercase text this function tries to identify the keyword “LG”.
a. If the keyword “LG” is present in the text, this function returns the text for further operations.
b. Else, it repeats calling the voicein function.
def take_alter_command():
def voicein():
CHUNK = 515
FORMAT = pyaudio.paInt16
CHANNELS = 2
RATE = 44100
RECORD_SECONDS = 5
WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME = "output.wav"
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(format=FORMAT,
channels=CHANNELS,
rate=RATE,
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=CHUNK)
print("* recording")
frames = []
for i in range(0, int(RATE / CHUNK * RECORD_SECONDS)):
data = stream.read(CHUNK)
frames.append(data)
print("* done recording")
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
p.terminate()
wf = wave.open(WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME, 'wb')
wf.setnchannels(CHANNELS)
wf.setsampwidth(p.get_sample_size(FORMAT))
wf.setframerate(RATE)
wf.writeframes(b''.join(frames))
wf.close()
from google.cloud import speech
import io
client = speech.SpeechClient()
speech_file = "/home/root/ObjectDetection/output.wav"
with io.open(speech_file, "rb") as audio_file:
content = audio_file.read()
audio = speech.RecognitionAudio(content=content)
config = speech.RecognitionConfig(
encoding=speech.RecognitionConfig.AudioEncoding.LINEAR16,
sample_rate_hertz=44100,
language_code="en-US",
audio_channel_count=2,
)
response = client.recognize(config=config, audio=audio)
# Each result is for a consecutive portion of the audio. Iterate through
# them to get the transcripts for the entire audio file.
if len(response.results) == 0:
return voicein()
else:
for result in response.results:
# The first alternative is the most likely one for this portion.
print(u"Transcript: {}".format(result.alternatives[0].transcript))
resultvoice = (format(result.alternatives[0].transcript))
resultvoice = resultvoice.lower()
if 'lg' in resultvoice:
outputvoice = resultvoice.replace('lg', '')
return outputvoice
else:
return take_alter_command()
return resultvoice
text = voicein()
return text;
run_lg()
This function helps processing user voice input and runs the YOLO DNN model to process the result.
- InputCommand calls the
take_alter_command function and takes the input from the user. - InputCommand converts the input text into lowercase and changes the exception words like “potted plant” to “pottedplant” as per
coco.names file. - The input text is then broken into single words and kept in a list named
ObjectToFind. - The YOLO configuration file and the weights file are then loaded by using DNN. This class allows to create and manipulate comprehensive artificial neural networks.
- All the names from the
coco.names file is then stored in a list named classes. - Then some operations to handle the camera are executed by using the camera2 service API.
- Then the captured images are processed and then the detected objects are labeled in those images accordingly.
- The processed images are stored locally.
- If the confidence is more than 0.5 (50%), then a rectangular box is created around the object with the object name and confidence score and the object name is added to the “items” list.
- The object detection app then shows the processed image with the rectangular box and labels.
def run_lg():
InputCommand = take_alter_command()
InputCommand = InputCommand.lower()
if "potted plant" in InputCommand:
InputCommand = InputCommand.replace("potted plant", "pottedplant")
if "tv monitor" in InputCommand:
InputCommand = InputCommand.replace("tv monitor", "tvmonitor")
if "dining table" in InputCommand:
InputCommand = InputCommand.replace("dining table", "diningtable")
ObjectToFind = []
ObjectToFind = (InputCommand.split())
net = cv2.dnn.readNet('yolov3.weights', 'yolov3.cfg')
classes = []
with open('coco.names', 'r') as f:
classes = f.read().splitlines()
os.system("luna-send -n 1 -f luna://com.webos.service.camera2/open '{"+'"id": "camera1"}'+"'"+">handle.txt")
f = open("handle.txt")
for i in f:
if "handle" in i:
h = i.replace('"handle":', '')
handle = h.replace(" ","")
os.system("luna-send -n 1 -f luna://com.webos.service.camera2/setFormat '{"+'"handle": '+str(handle)+',"params":{"width": 1920,"height": 1080,"format": "JPEG", "fps": 30}}'+"'")
os.system("luna-send -n 1 -f luna://com.webos.service.camera2/startPreview '{"+'"handle": '+str(handle)+', "params": {"type":"sharedmemory","source":"0"}}'+"'")
os.system("rm /home/root/ObjectDetection/picture/*")
os.system("luna-send -n 1 -f luna://com.webos.service.camera2/startCapture '{"+'"handle": '+str(handle)+',"params":{"width": 1920,"height": 1080,"format": "JPEG","mode":"MODE_ONESHOT","nimage":6},"path":"/home/root/ObjectDetection/picture"}'+"'")
os.system("ls /home/root/ObjectDetection/picture >imgName.txt")
f = open("imgName.txt")
val = 0
for i in f:
val = i
os.system("luna-send -n 1 -f luna://com.webos.service.camera2/stopPreview '{"+'"handle": '+str(handle)+"}'")
os.system("luna-send -n 1 -f luna://com.webos.service.camera2/close '{"+'"handle": '+str(handle)+"}'")
if "" in val:
val = val.replace("", "")
imgPath = '/home/root/ObjectDetection/picture/'+val
img = cv2.imread(imgPath)
height, width, _ = img.shape
center = (width/2)
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img, 1/255, (416, 416), (0,0,0), swapRB=True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
output_layers_names = net.getUnconnectedOutLayersNames()
layesOutputs = net.forward(output_layers_names)
boxes = []
confidences = []
class_ids = []
for output in layesOutputs:
for detection in output:
scores = detection[5:]
class_id = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[class_id]
if confidence > 0.5:
center_x = int(detection[0]*width)
center_y = int(detection[1]*height)
w = int(detection[2]*width)
h = int(detection[3]*height)
x = int(center_x - w/2)
y = int(center_y - h/2)
boxes.append([x, y, w, h])
confidences.append((float(confidence)))
class_ids.append(class_id)
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.5, 0.4)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN
colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(boxes), 3))
items = []
position = []
position2 = []
for i in indexes.flatten():
x, y, w, h = boxes[i]
label = str(classes[class_ids[i]])
items.append(label)
position.append(x)
position2.append(x+w)
confidence = str(round(confidences[i],2))
color = colors[i]
cv2.rectangle(img, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), color, 2)
cv2.putText(img, label +" "+ confidence, (x, y+20), font, 2, (255,255,255), 2)
cv2.imwrite('/media/internal/ObjectDetectionImage/image.jpg',img)
temp = ("luna-send -n 1 luna://com.webos.applicationManager/launch '{"+'"id":"com.app.objectviewer", "params":{"imagePath": "/media/internal/ObjectDetectionImage/image.jpg", "imageLabel": "Test Image"}}'+"'")
temp2 = ("luna-send -n 1 -f luna://com.webos.applicationManager/closeByAppId '{"+'"id":"com.app.objectviewer"}'+"'")
os.system(temp2)
os.system(temp)
ObjectToFindLen = len(ObjectToFind)
ObjectToFindCount = 0
f=0
p1 = 0
p2 = 0
duplicate_dict = Counter(items)
dis = ((center*15)/100)
for i in ObjectToFind:
ObjectToFindCount = ObjectToFindCount + 1
if i in classes:
if i in items:
f=1
TotalObject = duplicate_dict[i]
if TotalObject == 1:
coord = items.index(i)
if((position[coord] <= center) and (position2[coord] >= center)):
talk(i+" found in the center")
if((position[coord] < center) and (position2[coord] <= center)):
if (position2[coord] >= (center - dis)):
talk(i+" found in the left but close to the center")
elif (position[coord] <= dis):
talk(i+" found towards the left most end")
else:
talk(i+" found in the left middle")
if((position[coord] >= center) and (position2[coord] > center)):
if (position[coord] <= (center + dis)):
talk(i+" found in the right but close to the center")
elif (position2[coord] >= (width - dis)):
talk(i+" found towards the right most end")
else:
talk(i+" found in the right middle")
if TotalObject > 1:
talk("total "+str(TotalObject)+" "+i+" found")
w = 0
objcountLeftCenter = 0
objcountLeftMiddle = 0
objcountLeftEnd = 0
objcountRightCenter = 0
objcountRightMiddle = 0
objcountRightEnd = 0
objcountCenter = 0
for q in items:
if q == i:
if((position[w] <= center) and (position2[w] >= center)):
objcountCenter = objcountCenter + 1
if((position[w] < center) and (position2[w] <= center)):
if (position2[w] >= (center - dis)):
objcountLeftCenter = objcountLeftCenter + 1
elif (position[w] <= dis):
objcountLeftEnd = objcountLeftEnd + 1
else:
objcountLeftMiddle = objcountLeftMiddle + 1
if((position[w] >= center) and (position2[w] > center)):
if (position[w] <= (center + dis)):
objcountRightCenter = objcountRightCenter + 1
elif (position2[w] >= (width - dis)):
objcountRightEnd = objcountRightEnd + 1
else:
objcountRightMiddle = objcountRightMiddle + 1
w = w+1
talk("out of which ")
if objcountLeftCenter != 0:
talk(str(objcountLeftCenter)+" "+i+" found in the left but close to the center")
if objcountLeftMiddle != 0:
talk(str(objcountLeftMiddle)+" "+i+" found in the left middle")
if objcountLeftEnd != 0:
talk(str(objcountLeftEnd)+" "+i+" found towards the left most end")
if objcountRightCenter != 0:
talk(str(objcountRightCenter)+" "+i+" found in the right but close to the center")
if objcountRightMiddle != 0:
talk(str(objcountRightMiddle)+" "+i+" found in the right middle")
if objcountRightEnd != 0:
talk(str(objcountRightEnd)+" "+i+" found towards the right most end")
if objcountCenter != 0:
talk(str(objcountCenter)+" "+i+" found in the center")
else:
f=1
talk(i+" not found")
else:
if ObjectToFindCount == ObjectToFindLen:
s=0
for i in ObjectToFind:
s = s+1
if s <= (len(ObjectToFind) - 1):
val = (i+" "+ObjectToFind[s])
if val in classes:
if val in items:
f=1
TotalObject = duplicate_dict[val]
if TotalObject == 1:
coord = items.index(val)
if((position[coord] <= center) and (position2[coord] >= center)):
talk(val+" found in the center")
if((position[coord] < center) and (position2[coord] <= center)):
if (position2[coord] >= (center - dis)):
talk(val+" found in the left but close to the center")
elif (position[coord] <= dis):
talk(val+" found towards the left most end")
else:
talk(val+" found in the left middle")
if((position[coord] >= center) and (position2[coord] > center)):
if (position[coord] <= (center + dis)):
talk(val+" found in the right but close to the center")
elif (position2[coord] >= (width - dis)):
talk(val+" found towards the right most end")
else:
talk(val+" found in the right middle")
if TotalObject > 1:
talk("total "+str(TotalObject)+" "+val+" found")
w = 0
objcountLeftCenter = 0
objcountLeftMiddle = 0
objcountLeftEnd = 0
objcountRightCenter = 0
objcountRightMiddle = 0
objcountRightEnd = 0
objcountCenter = 0
for q in items:
if q == val:
if((position[w] <= center) and (position2[w] >= center)):
objcountCenter = objcountCenter + 1
if((position[w] < center) and (position2[w] <= center)):
if (position2[w] >= (center - dis)):
objcountLeftCenter = objcountLeftCenter + 1
elif (position[w] <= dis):
objcountLeftEnd = objcountLeftEnd + 1
else:
objcountLeftMiddle = objcountLeftMiddle + 1
if((position[w] >= center) and (position2[w] > center)):
if (position[w] <= (center + dis)):
objcountRightCenter = objcountRightCenter + 1
elif (position2[w] >= (width - dis)):
objcountRightEnd = objcountRightEnd + 1
else:
objcountRightMiddle = objcountRightMiddle + 1
w = w+1
talk("out of which ")
if objcountLeftCenter != 0:
talk(str(objcountLeftCenter)+" "+val+" found in the left but close to the center")
if objcountLeftMiddle != 0:
talk(str(objcountLeftMiddle)+" "+val+" found in the left middle")
if objcountLeftEnd != 0:
talk(str(objcountLeftEnd)+" "+val+" found towards the left most end")
if objcountRightCenter != 0:
talk(str(objcountRightCenter)+" "+val+" found in the right but close to the center")
if objcountRightMiddle != 0:
talk(str(objcountRightMiddle)+" "+val+" found in the right middle")
if objcountRightEnd != 0:
talk(str(objcountRightEnd)+" "+val+" found towards the right most end")
if objcountCenter != 0:
talk(str(objcountCenter)+" "+val+" found in the center")
else:
f=1
talk(val+" not found")
if s == (ObjectToFindLen -1) and f==0:
talk("Sorry no object found")
while True:
run_lg()




